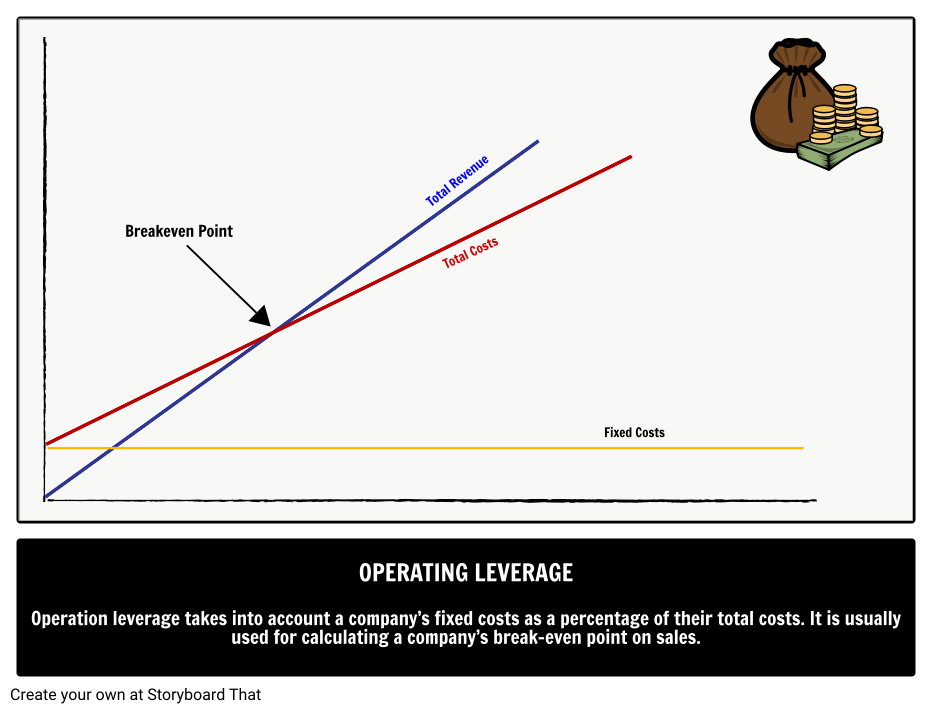
Financial leverage relates to Operating Leverage, which uses fixed costs to measure risk, by adding market volatility into the equation. First-order operational leverage affects income directly, whereas second-order or combined leverage affects income indirectly through fluctuations in asset values. In conclusion, the higher the operating leverage, the more the company’s income is influenced by fluctuations in sales volume.
Why is DOL important for investors?
But thanks to the internet, Inktomi’s software could be distributed to customers at almost no cost. After its fixed development costs were recovered, each additional sale was almost pure profit. In most cases, you will have the percentage change of sales and EBIT directly. The company usually provides those values on the quarterly and yearly earnings calls. Basically, you can just put the indicated percentage in our degree of operating leverage calculator, even while the presenter is still talking, and voilà. However, companies that need to spend a lot of money on property, plant, machinery, and distribution channels, cannot easily control consumer demand.
Core Financial Modeling
Conversely, retail stores tend to have low fixed costs and large variable costs, especially for merchandise. Because retailers sell a large volume of items and pay upfront for each unit sold, COGS increases as sales increase. For example, a software business has greater fixed costs in developers’ salaries and lower variable costs in software sales. In contrast, a computer consulting firm charges its clients hourly and doesn’t need expensive office space because its consultants work in clients’ offices. As the cost accountant in charge of setting product pricing, you are analyzing ABC Company’s fixed and variable costs and want to look at the degree of operating leverage.
Our Services
A high degree of operating leverage provides an indication that the company has a high proportion of fixed operating costs compared to its variable operating costs. It also means that the company can make more money from each additional sale while keeping its fixed costs intact. As a result, fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, acquire a higher value without incurring higher costs. At the end of the day, the firm’s profit margin can expand with earnings increasing at a faster rate than sales revenues.
- We will need to get the EBIT and the USD sales for the two consecutive periods we want to analyze.
- A higher proportion of fixed costs in the production process means that the operating leverage is higher and the company has more business risk.
- A higher operating leverage means the company has higher fixed costs, and a lower operating leverage means the company has higher variable costs.
- If you have the percentual change (period to period) of sales, put it here.
- As sales took a nosedive, profits swung dramatically to a staggering $58 million loss in Q1 of 2001—plunging down from the $1 million profit the company had enjoyed in Q1 of 2000.
Without a good understanding of the company’s inner workings, it is difficult to get a truly accurate measure of the DOL. While this is riskier, it does mean that every sale made after the break-even point will generate a higher contribution to profit. There are fewer variable costs in a cost structure with a high degree of operating leverage, and variable costs always cut into added productivity—though they also reduce losses from lack of sales. The degree of operating leverage can show you the impact of operating leverage on the firm’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). Also, the DOL is important if you want to assess the effect of fixed costs and variable costs of the core operations of your business.
John’s fixed costs are $780,000, which goes towards developers’ salaries and the cost per unit is $0.08. Given that the software industry is involved in the development, marketing and sales, it includes a range of applications, from network systems and operating management tools to customized software for enterprises. Companies with a low DOL have a higher proportion of variable costs that depend on the what is unearned revenue top faqs on unearned revenue number of unit sales for the specific period while having fewer fixed costs each month. However, since the fixed costs are $100mm regardless of the number of units sold, the difference in operating margin among the cases is substantial. Operating leverage is the ratio of a business’s fixed costs to its variable costs. This ratio is often used when forecasting sales and determining appropriate prices.
Therefore, poor managerial decisions can affect a firm’s operating level by leading to lower sales revenues. One concept positively linked to operating leverage is capacity utilization, which is how much the company uses its resources to generate revenues. Increasing utilization infers increased production and sales; thus, variable costs should rise.
If fixed costs remain the same, a firm will have high operating leverage while operating at a higher capacity. Operating leverage is a cost-accounting formula (a financial ratio) that measures the degree to which a firm or project can increase operating income by increasing revenue. A business that generates sales with a high gross margin and low variable costs has high operating leverage.
But this comes out to only a $9mm increase in variable costs whereas revenue grew by $93mm ($200mm to $293mm) in the same time frame. In addition, in this scenario, the selling price per unit is set to $50.00, and the cost per unit is $20.00, which comes out to a contribution margin of $300mm in the base case (and 60% margin). If sales and customer demand turned out lower than anticipated, a high DOL company could end up in financial ruin over the long run. As a result, companies with high DOL and in a cyclical industry are required to hold more cash on hand in anticipation of a potential shortfall in liquidity. This information shows that at the present level of operating sales (200 units), the change from this level has a DOL of 6 times. This variation of one time or six-time (the above example) is known as degree of operating leverage (DOL).
To lower your DOL, consider reducing fixed costs, increasing variable costs, or adjusting your cost structure to make it more flexible in response to sales changes. An operating leverage under 1 means that a company pays more in variable costs than it earns from each sale. Companies facing this will need to raise prices or work to reduce variable costs to bring operating leverage above 1. Looking back at a company’s income statements, investors can calculate changes in operating profit and sales. Investors can use the change in EBIT divided by the change in sales revenue to estimate what the value of DOL might be for different levels of sales. This allows investors to estimate profitability under a range of scenarios.